Charging an air conditioner using vapour pressure readings is a complex process that requires specialised knowledge and tools. It involves carefully monitoring pressures on both the high and low sides of the system to ensure the correct amount of refrigerant is added. This is done by adding refrigerant slowly, observing pressure changes, and adjusting the charge until the system’s operating pressures are within the manufacturer’s specifications.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
Understanding Vapour Pressure and Refrigerant Charge:
- Vapour Pressure:
The pressure exerted by a vapour in equilibrium with its condensed phase at a given temperature. In AC systems, this refers to the pressure of the refrigerant vapour in the suction line (low side) and the condenser (high side).
- Refrigerant Charge:
The amount of refrigerant in the system. An incorrect charge can lead to various issues, including reduced cooling capacity, compressor failure, and inefficient operation.
Steps Involved in Charging by Vapour Pressure:
- 1. Prepare the System:
- Ensure the AC unit is running and stable.
- Attach pressure gauges to the service valves (high and low side).
- Install temperature sensors on the suction line and liquid line.
- 2. Read and Interpret Pressures:
- Low-Side Pressure: This is the pressure of the refrigerant vapour on the suction side. It indicates the system’s low-side temperature and charge level.
- High-Side Pressure: This is the pressure of the refrigerant vapour on the high side (condenser). It indicates the system’s high-side temperature and charge level.
- 3. Adding Refrigerant:
- Liquid or Vapour: Refrigerant can be added as either a liquid or a vapour, depending on the specific refrigerant and system design.
- Slow and Controlled Addition: Refrigerant is added slowly to avoid overloading the system or causing slugging (liquid refrigerant entering the compressor).
- Monitoring Pressure Changes: Continuously monitor the pressure gauges while adding refrigerant.
- Adjusting the Charge: Add or remove refrigerant as needed to bring the pressures within the desired range.
- 4. Checking for Proper Operation:
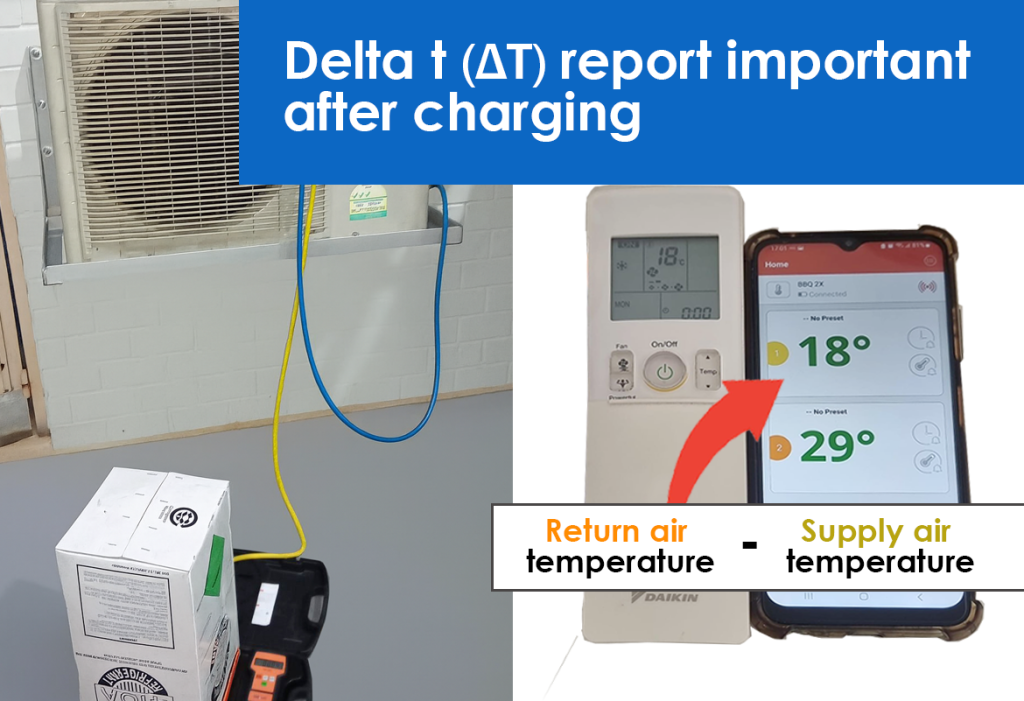
- Superheat and Subcooling: After charging, the technician will use superheat and subcooling readings to confirm that the refrigerant charge is correct.
- System Performance: The AC unit is allowed to run for a period to ensure it is cooling properly
- 5. Final Steps:
- Disconnect Gauges: Once the correct pressures and readings are achieved, the gauges are safely disconnected.
- Check for Leaks: A leak check is recommended after charging, especially if a significant amount of refrigerant was added.
Important Considerations for Charging an Air Conditioner:
- Proper Tools and Equipment: This process requires specialised tools like pressure gauges, temperature sensors, and a refrigerant recovery machine (if applicable).
- Safety: Handling refrigerant requires proper safety precautions and training.
- Manufacturer’s Specifications: Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications for the specific AC unit being charged, as they will outline the recommended pressures and refrigerant charge.




Leave a Reply